The FDA has released a draft of new recommendations aimed at improving the performance accuracy of pulse oximeters, particularly across varied skin pigments. The key elements include:
- Collecting Clinical Data: Emphasis on assessing device accuracy across different skin tones.
- Broadened Participant Pool: Increasing the number of individuals in clinical studies for more comprehensive data.
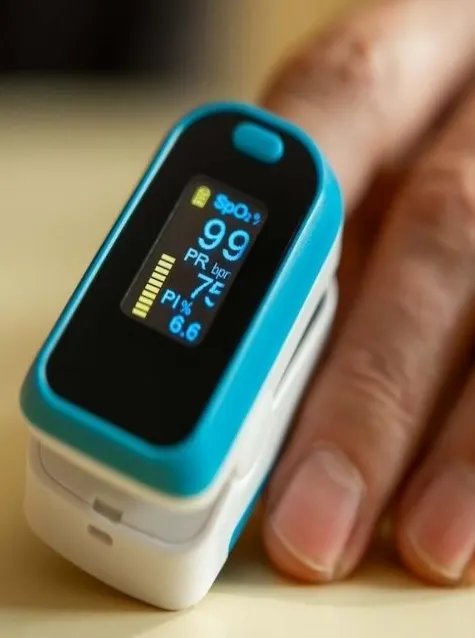

- Standardized Assessment Methods: Implementing both subjective (Monk Skin Tone Scale) and objective (individual typology angle) techniques for evaluating skin tone.
- Premarket Submission Updates: Devices that demonstrate performance accuracy should include a clear labeling statement, ensuring users know they maintain consistent accuracy across diverse populations.


Johnson & Johnson has paused the U.S. rollout of its Varipulse heart device following four reported stroke incidents, including one in a clinical study. At least two similar cases were reported in Europe. The company initiated the pause on January 5, after completing over 130 cases as part of the U.S. launch. Varipulse, which uses pulsed field ablationto treat abnormal
heart rhythms, was FDA-approved in November. The device’s rollout had also been paused internationally last year, with mixed feedback from doctors. J&J did not specify when it expects to resume the launch but said it is investigating the issue. The pause led to a 3% drop in J&J’s stock. J&J confirmed that commercial activities and cases outside the U.S. would continue unaffected by the pause.

In January 2025, the FDA released a draft guidance titled “Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Device Software Functions: Lifecycle Management and Marketing Submission Recommendations.” The guidance aims to help manufacturers manage iterative improvements and lifecycle

changes to AI-enabled device software while maintaining regulatory compliance. It outlines recommendations for marketing submissions, including predefined change control plans and validation strategies to ensure continued device safety and effectiveness. This draft guidance supports innovation while streamlining regulatory processes for AI-driven devices.

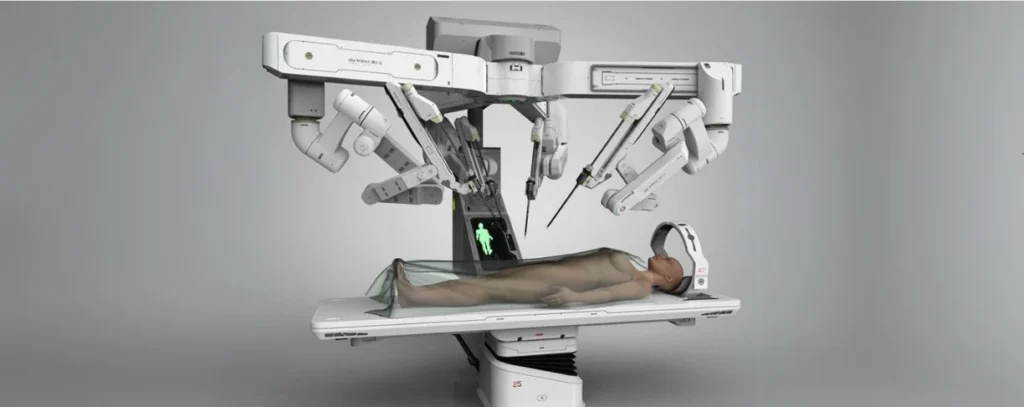
Intuitive, a global leader in robotic-assisted surgery and minimally invasive care, has announced plans to establish direct operations in Italy, Spain, and Portugal. By transitioning from third-party distributors to direct operations, Intuitive aims to strengthen customer relationships, enhance service capabilities,
and broaden access to its advanced technologies. The company’s flagship innovations, including the da Vinci® Surgical System, used in complex surgeries, and the Ion® Endoluminal System, designed for minimally invasive lung biopsies, will be more readily available to medical professionals across these key European markets.

The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) has issued a draft for the updation of the existing risk-based classification list for medical devices, dated 06 January 2025, for stakeholder comments. This revision aims to

enhance the categorization of devices based on their risk level, ensuring greater patient safety and regulatory compliance. The draft update reflects CDSCO’s efforts to refine the classification system in line with evolving industry practices. Stakeholders are encouraged to review and provide their feedback to contribute to the finalization of the revised risk-based classification list, which will be instrumental in regulatory decision-making.

The FDA has issued a recall for Hologic’s BioZorb 3D bioabsorbable markers due to concerns about potential health risks for patients. The markers, which are used in breast cancer treatment to mark tissue for surgical reference, may not fully dissolve as intended. This could lead to the device remaining

in the body longer than expected, potentially causing complications such as inflammation or infection.
Hologic has removed these devices from the market, and healthcare providers are instructed to stop using them and to follow up with patients who have had them implanted. The FDA continues to monitor the situation to safeguard public health.

- The FDA has granted traditional marketing authorization to specific COVID-19 tests, including molecular, antigen, and antibody tests, after they successfully met the agency’s rigorous standards for safety, effectiveness, and performance.

- This transition from Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) to full approval means the tests have undergone a more comprehensive review, ensuring their reliability and public health safety.
- The FDA will continue to monitor these tests to ensure ongoing performance and safety in the market, underscoring its commitment to providing accurate and dependable COVID-19 detection tools

Selecting the right predicate device is a cornerstone of a successful 510(k) premarket notification submission, as highlighted in this article by Alceon Medtech Consulting. The predicate device serves as a benchmark to prove that your medical device’s substantial equivalence to one legally marketed, a key requirement for FDA clearance.
The article outlines critical best practices for this selection process. It recommends a deep dive into FDA databases and guidance documents to identify predicates that match your device in intended use, technological characteristics, and performance. It warns against choosing predicates with significant differences that might trigger complex regulatory challenges or additional testing. A systematic evaluation of the predicate’s data, such as labelling, clinical

performance, and technological specifications, is essential to avoid costly delays. By following these practices, manufacturers can mitigate risks, streamline their regulatory pathway, and increase the likelihood of a smooth and timely FDA review process.